
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have revolutionized investing by combining the diversification of mutual funds with the ease of trading stocks. These funds track indexes, commodities, bonds, or a basket of assets like an index fund but trade like a stock on an exchange. This guide delves into strategies for trading ETFs, selecting the right ETFs for your portfolio, and understanding the benefits they offer.
How to Choose ETFs: A Detailed Approach
Selecting the right Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a critical decision that can influence the success of your investment portfolio. As you navigate through the plethora of ETFs available in the market, it’s essential to align your choices with your investment philosophy, goals, and risk tolerance. Warren Buffett, one of the most successful investors of our time, once said, “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” This wisdom underscores the importance of making informed choices, particularly when it comes to selecting ETFs that fit your investment strategy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing ETFs
To make an informed decision, consider the following detailed factors:
- Expense Ratio: The expense ratio represents the annual cost of owning an ETF, expressed as a percentage of the fund’s assets. While it might seem minimal at first glance, the expense ratio can significantly impact your long-term investment returns. As Buffett emphasizes the value of cost-conscious investing, look for ETFs with lower expense ratios to ensure more of your money is working for you, not just funding management fees.
- Trading Volume: The liquidity of an ETF is indicated by its trading volume. ETFs with higher trading volumes typically have tighter bid-ask spreads, which means you’re more likely to buy and sell shares closer to the market price. This can reduce trading costs, making it easier to enter and exit positions efficiently.
- Tracking Error: The tracking error measures how closely an ETF follows its benchmark index. A lower tracking error means the ETF does a better job mirroring the performance of the index it tracks, which is crucial for investors looking for specific market exposures. It reflects the fund manager’s effectiveness in minimizing deviations from the index, ensuring your investment closely aligns with your targeted market performance.
- Underlying Assets: Understanding the composition of the ETF is paramount. The assets held within the ETF, whether they’re stocks, bonds, commodities, or a mix, should reflect your investment goals and strategy. Diving deep into the ETF’s holdings allows you to assess the diversity, quality, and risk associated with the fund, ensuring it matches your investment objectives.
Aligning ETF Selection with Your Investment Philosophy
Incorporating these considerations into your ETF selection process not only aligns with the prudent advice of seasoned investors like Buffett but also sets a solid foundation for building a diversified and resilient investment portfolio. By focusing on cost efficiency, liquidity, accuracy in tracking, and a thorough understanding of the ETF’s constituents, you position yourself to make choices that resonate with your long-term financial aspirations.
In conclusion, the selection of ETFs demands a thoughtful approach, emphasizing the importance of research, clarity of investment goals, and an understanding of market mechanisms. As you sift through the options, let the insights of the investment greats guide you and remember that the most informed decisions come from a place of knowledge and strategic thinking.
ETF Trading Strategies
Trading Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offers flexibility and access to a variety of investment strategies. Whether you’re a novice investor or a seasoned trader, understanding and employing the right ETF trading strategies can significantly impact your portfolio’s performance. Let’s delve into more detailed explanations of some effective ETF trading strategies:
Buy and Hold: A Foundation for Stability
The buy-and-hold strategy is a testament to the philosophy of investing with patience and foresight. It involves selecting ETFs that track broad market indexes, specific sectors, or thematic investments you believe have strong long-term growth potential. The key is to invest in ETFs representing areas of the economy that are expected to grow or remain stable over time, such as technology, healthcare, or green energy sectors. This strategy benefits from compound interest over time and is particularly suited to those with a longer investment horizon and a preference for lower turnover and potentially lower tax implications.
Sector Rotation: Timing the Economic Cycles
Sector rotation is a dynamic strategy that leverages cyclical economic trends. Investors systematically shift their allocations from one sector to another based on the current phase of the economic cycle. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or recession, funds might be moved into defensive sectors like utilities or consumer staples, which tend to be less sensitive to economic downturns. Conversely, during economic recovery or expansion phases, investments could shift towards more cyclical sectors such as consumer discretionary or technology, which are likely to benefit from increased economic activity. This strategy requires vigilance and a keen understanding of economic indicators and sector performance patterns.
Swing Trading: Capitalizing on Volatility
Swing trading ETFs is a strategy designed to take advantage of short- to medium-term price movements. It involves holding ETFs for a period ranging from a few days to several weeks to capture market gains based on volatility. Swing traders utilize technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points, relying on chart patterns, momentum indicators, and other technical tools to make informed decisions. This approach is more active and requires a good grasp of market timing and risk management to safeguard against sudden market movements.
Hedging: Protecting Against Downside Risk
Hedging with ETFs is a strategy employed to offset potential losses in your investment portfolio. Investors can use various ETFs, such as inverse ETFs, which are designed to perform inversely to their benchmark index, or ETFs that focus on assets inversely correlated with their portfolio holdings. For instance, if you hold a significant position in tech stocks and anticipate a sector downturn, you might invest in an inverse ETF that gains when the tech sector falls. This strategy is akin to taking out an insurance policy on your portfolio, mitigating risk during volatile or bearish market conditions.
Each of these strategies offers a unique way to engage with the ETF market, from the stability and simplicity of buy-and-hold to the more active approaches of sector rotation and swing trading, and the protective measures of hedging. Understanding these strategies and how they fit within your overall investment goals and risk tolerance is crucial to navigating the ETF landscape effectively. Remember, the best strategy is one that aligns with your investment objectives, time horizon, and comfort with market risk.
Benefits of ETF Trading
- Diversification: ETFs provide exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing individual investment risks.
- Flexibility: They can be bought and sold like stocks, offering investors flexibility in managing their portfolios.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, ETFs have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
Visual Insights: The Landscape of ETF Investment
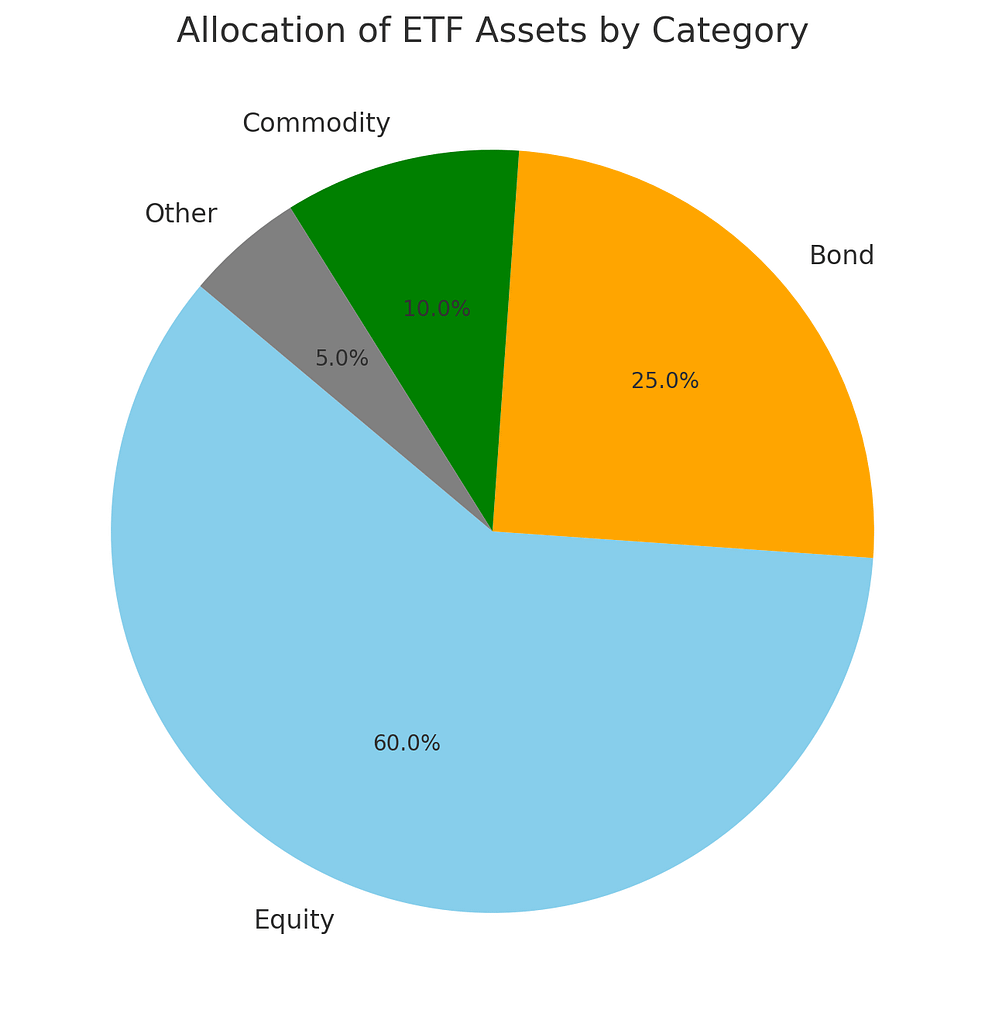
Pie Chart: Allocation of ETF Assets by Category
This pie chart shows the distribution of ETF assets across different categories, with equity ETFs dominating the market at 60%. Bonds come in second at 25%, followed by commodities at 10%, and other categories making up the remaining 5%.
This distribution highlights the strong preference among investors for equity ETFs, likely due to their potential for higher returns and the diversity they offer in portfolio construction.
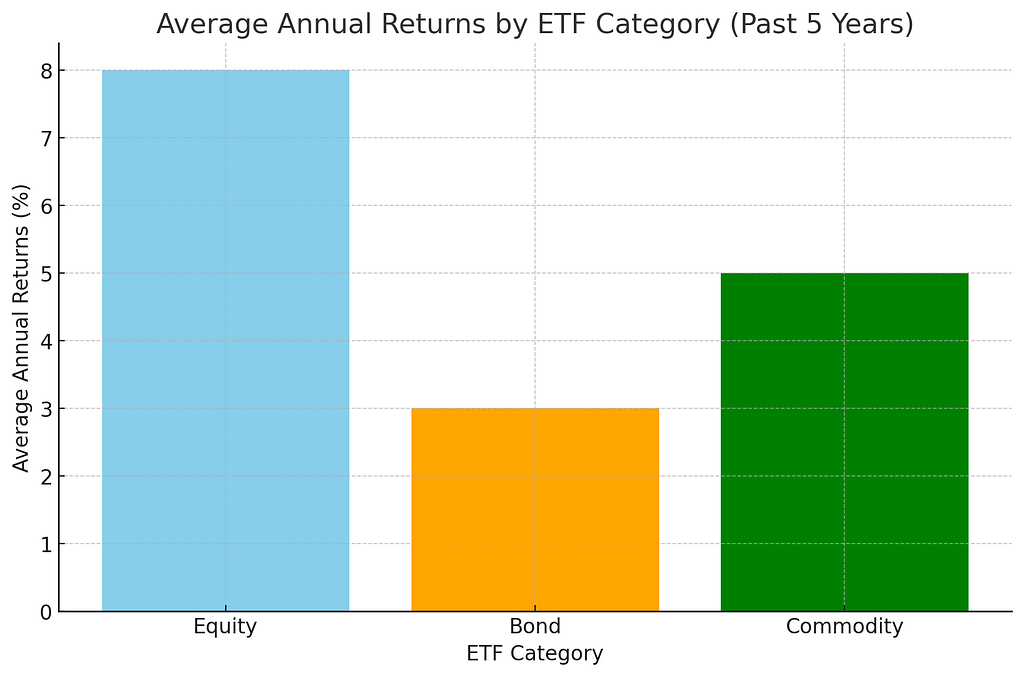
Bar Graph: Average Annual Returns by ETF Category (Past 5 Years)
The bar graph presents the average annual returns for ETFs across various categories over the past five years. Equity ETFs lead with an average return of 8%, underscoring their appeal to investors looking for growth. Commodity ETFs follow with a 5% return, offering a mix of risk and potential for returns, while bond ETFs provide a more conservative return of 3%, reflecting their role as a stabilizing element in investment portfolios.
This performance data provides valuable insights into the risk-return profile of different ETF categories, aiding investors in making informed decisions.
The Strategic Importance of ETFs in an Investment Portfolio
In the ever-evolving world of investment, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have emerged as pivotal instruments for investors aiming to construct diversified, resilient, and growth-oriented portfolios. Their strategic importance cannot be overstated, as ETFs offer a unique blend of features that cater to a broad spectrum of investment objectives, from capital preservation to aggressive growth. Let’s explore the multifaceted role ETFs play in enhancing investment portfolios.
Diversification Beyond Borders
ETFs are renowned for their ability to offer instant diversification across various asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions. This diversification is crucial in mitigating risks associated with market volatility and specific sector downturns. For instance, an investor looking to balance a portfolio heavily concentrated in U.S. equities might incorporate international ETFs to gain exposure to emerging markets or developed economies elsewhere. This global diversification not only spreads risk but also opens the door to opportunities in faster-growing economies.
Flexibility for Tactical Asset Allocation
The ease of trading ETFs allows investors to implement tactical asset allocation strategies effectively. As market conditions change, investors can adjust their exposure to different asset classes, sectors, or themes by simply buying or selling ETFs, much like individual stocks. This flexibility enables investors to capitalize on short-term market movements or adjust their investment strategy in response to economic forecasts or changes in interest rates, thereby optimizing portfolio performance.
Cost-Efficient Exposure to Various Investment Themes
With typically lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds, ETFs offer a cost-effective way to access a wide range of investment themes and strategies. Whether it’s following a broad market index, investing in specific industries like technology or renewable energy, or implementing strategies such as value or growth investing, ETFs allow investors to execute sophisticated investment strategies without incurring high management fees. This cost efficiency is particularly beneficial for long-term investors, as lower fees translate directly into higher net returns.
Enhancing Portfolio Performance with Specialized ETFs
The versatility of ETFs extends to specialized products designed to address specific investor needs, including leveraged ETFs for magnified exposure to market movements, inverse ETFs for hedging purposes, and fixed-income ETFs for stable income generation. These specialized ETFs can play a critical role in fine-tuning portfolio performance, offering tools for risk management, income generation, and capital appreciation.
The Role of ETFs in Modern Portfolios
The integration of ETFs into investment portfolios reflects a strategic approach to modern investing, where efficiency, flexibility, and diversification are paramount. By leveraging ETFs, investors can achieve a well-rounded investment portfolio that not only withstands market fluctuations but also capitalizes on global opportunities. The importance of ETFs in investment portfolios lies in their ability to democratize access to diversified investments, enabling both novice and experienced investors to build sophisticated portfolios that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
In conclusion, ETFs represent a cornerstone of contemporary investment strategy, offering unparalleled diversification, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Their strategic importance in investment portfolios is evident in their growing popularity and their role in enabling investors to navigate the complexities of the global markets with confidence and clarity.
Personal Insights: Navigating the World of ETFs
I’ve seen firsthand the transformative impact ETFs have had on investing. They offer a blend of accessibility, efficiency, and flexibility that is unmatched in the financial markets. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, the key to successful ETF investing lies in thorough research and a clear understanding of your investment goals.
From my experience, a diversified ETF portfolio, tailored to your risk tolerance and investment horizon, can serve as a cornerstone of your investment strategy. The ability to trade ETFs across various sectors and asset classes allows for strategic adjustments in response to changing market conditions, making them an invaluable tool for both strategic and tactical asset allocation.
In essence, ETFs democratize investing, providing access to asset classes and strategies that were once the domain of sophisticated investors. However, like any investment, they require due diligence and an understanding of the market dynamics at play. By leveraging the strategies outlined above and staying informed about market trends, investors can harness the power of ETFs to achieve their financial objectives.