
Commodity trading, a fundamental component of the global financial markets, involves the buying and selling of raw materials or primary products. This trading sector offers diverse opportunities, from hedging against inflation to speculation for profits. This exploration covers the types of commodities traded, market analysis techniques, and strategic approaches to navigating the commodity markets.
Types of Commodities Traded
Commodities are typically classified into two main categories: hard and soft commodities. Hard commodities are natural resources extracted or mined, whereas soft commodities include agricultural products or livestock.
Key Commodities
- Hard Commodities: Oil, gold, natural gas, and iron ore.
- Soft Commodities: Wheat, cotton, soybeans, and live cattle.
Market Analysis in Commodity Trading
Market analysis is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Two primary approaches are fundamental and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis
Focuses on external factors influencing commodity prices, such as weather conditions affecting agricultural products or geopolitical events impacting oil prices.
Technical Analysis
Relies on historical price data and chart patterns to predict future market movements. It’s widely used for timing entries and exits in the market.
Strategic Approaches to Commodity Trading
Successful commodity trading requires a solid strategy, combining market analysis with risk management techniques.
Common Strategies
- Buy and Hold: A long-term investment strategy based on the expectation that the commodity’s price will increase over time.
- Hedging: Involving the use of derivative instruments like futures and options to protect against price volatility.
- Speculation: Taking advantage of market trends and volatility to make short-term profits.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential in commodity trading due to the market’s inherent volatility. Key practices include diversification, setting stop-loss orders, and proper leverage use.
Visual Insights: Commodity Trading Landscape
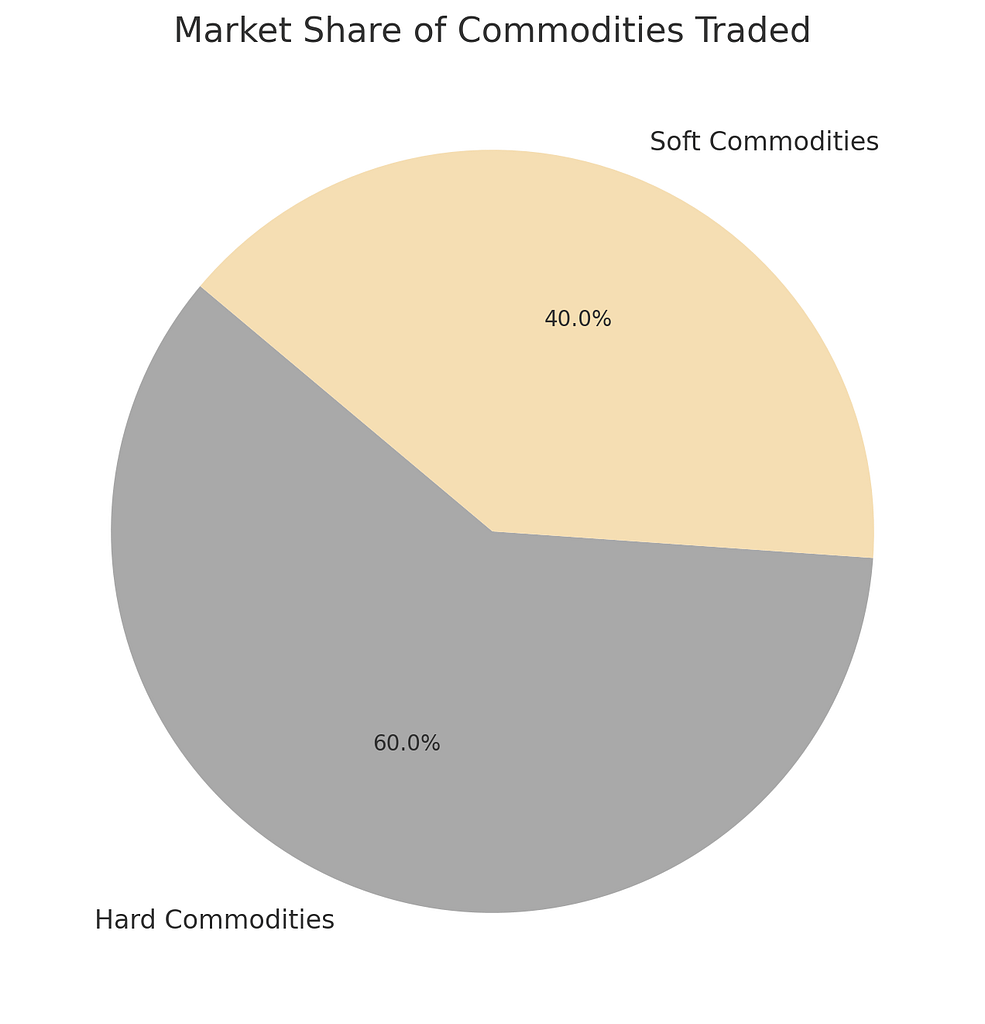
Pie Chart: Market Share of Commodities Traded
This pie chart shows the distribution of market share between hard and soft commodities, with hard commodities holding a dominant 60% share.
This dominance is attributed to their critical role in the global economy and the higher volatility they present, which attracts traders looking for profit opportunities.
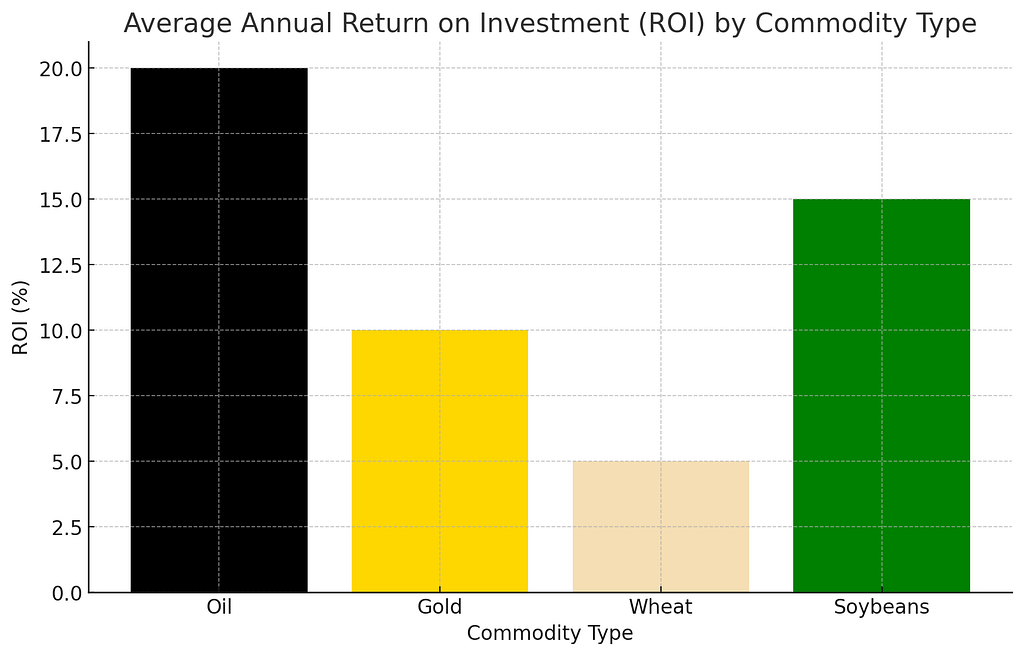
Bar Graph: Average Annual Return on Investment (ROI) by Commodity Type
The bar graph illustrates the varying average annual ROI across different commodity types, including oil, gold, wheat, and soybeans.
Oil and soybeans exhibit higher returns at 20% and 15%, respectively, indicating their significant market demand and price volatility.
Gold offers a 10% return, serving as a stable investment option during times of economic uncertainty, while wheat provides a 5% return, reflecting its essential but more stable market position.
These visuals highlight the potential profitability and risk associated with commodity trading, guiding investors in making informed decisions.
Informed Perspective on the Dynamics of Commodity Trading
The world of commodity trading is fascinating and complex, offering a unique blend of challenges and opportunities. Its appeal lies in the diversity of assets available for trade, each influenced by a distinct set of global factors, from geopolitical events to seasonal cycles. This variability can introduce significant volatility, presenting both risk and reward for traders.
From an analytical standpoint, commodity trading demands a keen understanding of both fundamental and technical analysis. Fundamental factors such as weather events, political instability, and economic policies can drastically affect commodity prices, highlighting the importance of staying informed about global news and trends. Meanwhile, technical analysis allows traders to navigate this volatility by identifying patterns and signals that suggest potential market movements.
Strategically, successful commodity trading hinges on a balanced approach that combines market insight with robust risk management practices. The volatile nature of commodities can lead to substantial gains but also significant losses. Therefore, employing strategies such as diversification, hedging, and the prudent use of leverage is crucial in mitigating risks while capitalizing on trading opportunities.
In essence, commodity trading represents a dynamic segment of the financial markets, replete with potential for those who invest the time to understand its intricacies. Whether viewed as a mechanism for portfolio diversification, a hedge against inflation, or a speculative endeavor, it commands respect for the forces that drive it and a disciplined approach to navigate its challenges.
Conclusion
The world of commodity trading offers a wealth of opportunities for those willing to navigate its complexities. By understanding the types of commodities traded, employing thorough market analysis, and implementing strategic approaches tailored to individual goals and risk tolerance, traders can capitalize on the opportunities presented by the commodity markets. Success in commodity trading requires continuous learning, adaptability, and a disciplined approach to risk management.