
Algorithmic trading, a method that uses computer algorithms to execute trades at speeds and volumes impossible for human traders, has significantly transformed the landscape of financial markets. This approach leverages complex mathematical models to make trading decisions, often based on price, timing, quantity, and many other mathematical indicators. Its rise represents a shift towards automation, efficiency, and precision in trading strategies.
Algorithmic trading is revolutionizing industries and driving revenue growth, particularly in the financial markets. The global Algorithmic Trading market is experiencing transformative trends due to technological advancements and the rise of artificial intelligence. A market analysis report reveals rapid growth trends, with the Algorithmic Trading market projected to reach USD 15.76 billion in 2023, showcasing significant growth potential
Understanding Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo-trading, automates the trading process by following a set of pre-defined instructions for placing trades. The objective is to achieve optimal execution, maximize profits, and minimize costs and slippage. This method is popular among institutional investors and hedge funds but is also accessible to retail traders through modern trading platforms.
Key Benefits
- Speed: Algorithms can execute orders within fractions of a second, much faster than human traders.
- Accuracy: Reduces the risk of manual errors in placing trades.
- Efficiency: Can scan and exploit trading opportunities across multiple markets and assets simultaneously.
- Discipline: Trading strategies are executed precisely without the influence of human emotions.
How It Works
Algorithmic trading involves the following key components:
- Market Data Analysis: Algorithms analyze real-time and historical data to identify trading opportunities.
- Strategy Formulation: Traders develop strategies based on patterns identified from data analysis.
- Backtesting: Strategies are tested on historical data to ensure their viability before live execution.
- Execution: Algorithms automatically execute trades according to the strategy, adjusting in real-time to market conditions.
Common Strategies
- Arbitrage Opportunities: Buying and selling equivalent securities in different markets to profit from price differences.
- Trend Following: Strategies that aim to capitalize on market trends, using indicators like moving averages.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Involves making thousands of trades within seconds to exploit small price discrepancies.
Impact on the Markets

Algorithmic trading has both supporters and critics. Proponents argue that it enhances market liquidity and narrows bid-ask spreads, making trading more efficient for everyone. Critics, however, contend that it can lead to market volatility and flash crashes, where prices plummet and recover rapidly without apparent reason.
The Role of Algorithmic Trading in Market Dynamics
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Efficiency | Enhances liquidity and reduces transaction costs. |
| Volatility | Can contribute to rapid price changes and instability in markets. |
| Accessibility | Levels the playing field by making sophisticated strategies available to a wider audience. |
Visual Insights
To illustrate the significance of algorithmic trading, consider the following visual representations:
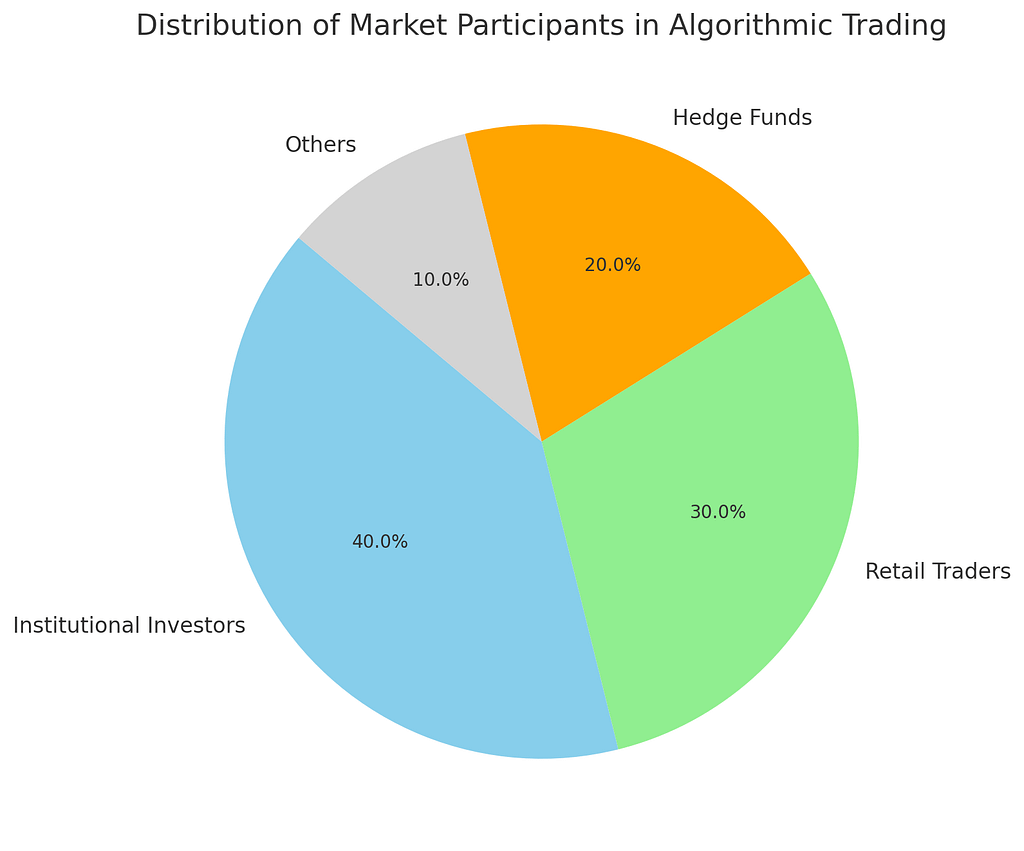
- Pie Chart: Distribution of Market Participants in Algorithmic Trading
- Institutional Investors: 40%
- Retail Traders: 30%
- Hedge Funds: 20%
- Others: 10%
This pie chart shows that institutional investors and retail traders are the primary participants in algorithmic trading, highlighting its widespread adoption across different market players.
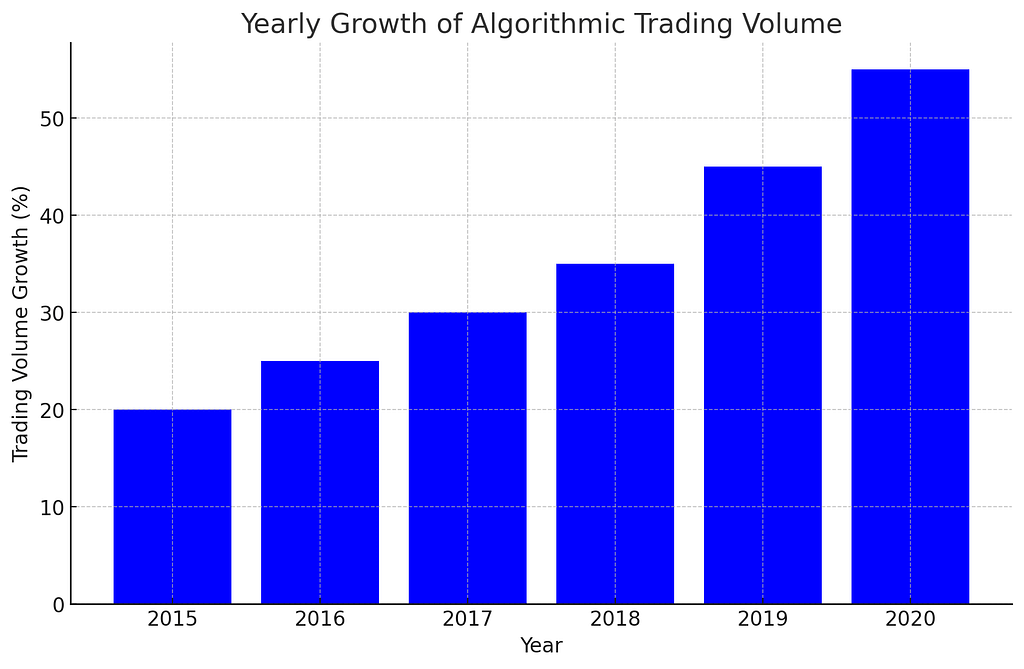
- Bar Graph: Yearly Growth of Algorithmic Trading Volume
- The graph would depict a steady increase over the years, illustrating the growing dominance of algorithmic trading in financial markets.
Conclusion
Algorithmic trading represents a significant evolution in the way financial markets operate, offering both opportunities and challenges. By automating the trading process, it promises greater efficiency, accuracy, and speed, but it also requires rigorous risk management and oversight to mitigate potential downsides. As technology advances, the role of algorithmic trading is likely to expand, further revolutionizing market dynamics and trading strategies.