
Market makers play a critical role in the trading ecosystem, ensuring liquidity and facilitating the continuous exchange of assets in financial markets. Their function is vital for the smooth operation of both equity and derivatives markets, affecting pricing, liquidity, and overall market efficiency. This article explores the function of market makers, their impact on liquidity and pricing, and their importance in the trading world.
Understanding Market Makers
Market makers represent a cornerstone of the trading ecosystem, functioning as intermediaries that facilitate the smooth flow of financial markets. They are typically financial institutions, brokerage firms, or individual traders committed to offering continuous bid and ask prices for specific securities or financial instruments. This continuous presence in the market ensures that other participants can buy and sell these assets with ease, promoting an environment where trades can be executed swiftly and efficiently.
The Role and Mechanisms of Market Making
At its core, the role of a market maker is to ensure that there is always a buyer and a seller for securities in the market, thereby “making a market.” This role is crucial in both primary markets, where securities are first issued, and secondary markets, where securities are traded among investors. Market makers achieve this by maintaining an inventory of securities and standing ready to buy or sell them at publicly quoted prices.
Profitability and the Bid-Ask Spread
Market makers profit through the bid-ask spread—the difference between the price at which they buy securities (the bid price) and the price at which they sell them (the ask price). This spread compensates them for the risk associated with holding a position in a particular security and provides an incentive for maintaining market liquidity. The size of the spread can vary depending on the security’s liquidity, with more liquid securities typically having narrower spreads.
Key Responsibilities
- Providing Liquidity: Market makers play a pivotal role in ensuring that there is always a buyer for every seller and vice versa. This liquidity is fundamental to the efficient functioning of financial markets, as it allows participants to enter and exit positions without causing significant price movements. Liquidity also contributes to lower transaction costs and better price discovery, benefiting all market participants.
- Setting Bid-Ask Spreads: By determining the bid and ask prices, market makers directly influence the market’s liquidity and efficiency. The spread between these prices reflects not only the market maker’s compensation but also market conditions such as volatility, trading volume, and the underlying security’s liquidity. Market makers adjust these spreads in response to changing market conditions to manage their risk while continuing to provide liquidity.
- Facilitating Price Discovery: Through their trading activities, market makers contribute to the process of price discovery, helping the market find equilibrium prices for securities based on supply and demand dynamics. Their continuous quoting of bid and ask prices provides valuable information to the market, reflecting the latest developments and expectations.
Market Makers and Market Stability
In addition to their primary roles, market makers indirectly contribute to market stability. By providing continuous trading opportunities, they help dampen price volatility, especially in times of market stress or uncertainty. This stabilizing effect is crucial during turbulent market periods, as it ensures that the market remains orderly and functional, allowing investors to trade based on their assessments of value rather than the mechanics of market liquidity.
Understanding the role and mechanisms of market making is essential for anyone participating in the financial markets. Market makers not only ensure liquidity and facilitate trades but also play a significant role in setting prices and contributing to overall market stability. Their activities enable the efficient operation of financial markets, benefiting traders, investors, and the broader economy.

Impact on Liquidity and Pricing
Market makers enhance market liquidity, making it easier for investors to enter and exit positions. They absorb market fluctuations, reducing price volatility by providing a constant demand and supply for securities.
Liquidity Enhancement
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Increased liquidity leads to narrower bid-ask spreads, lowering the cost of trading.
- Improved Market Efficiency: Constant price quotations by market makers help in the accurate valuation of securities.
The Crucial Role of Market Makers in the Trading Ecosystem: An In-Depth Look
The fabric of the financial trading ecosystem is intricately woven with various participants, among which market makers occupy a pivotal role. Their contribution is fundamental to the operational efficiency and stability of markets, facilitating the seamless execution of trades and enhancing the process of price discovery. Understanding the depth of their impact can provide insights into the mechanics of trading and the maintenance of an orderly market.
Expanded Importance in the Trading Ecosystem
Market makers stand at the core of the trading world, ensuring that financial markets operate smoothly and efficiently. By committing to buy and sell securities at any given time, they provide the necessary liquidity and depth that allow other market participants to trade with ease, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with finding a buyer or seller for securities.
Smoother Price Discovery
Price discovery is a critical process in financial markets, where the prices of securities are determined based on supply and demand dynamics. Market makers facilitate this process by continuously posting bid and ask prices based on their assessment of a security’s value and prevailing market conditions. This constant flow of information helps integrate new data into prices, ensuring they accurately reflect the latest market sentiment and information. Consequently, market makers enable markets to adjust more swiftly to new developments, ensuring prices remain fair and transparent.
Quick Absorption of New Information
In a world where financial news can change the market landscape in seconds, the ability of markets to quickly absorb and reflect new information is paramount. Market makers play a crucial role in this aspect by adjusting their pricing strategies in response to new information, thus facilitating its rapid incorporation into market prices. This responsiveness ensures that securities’ prices are always aligned with their true market value, based on the most current information available.
Roles and Benefits
Enhancing Market Stability
Market makers contribute significantly to the stabilization of markets, especially during periods of high volatility. By ensuring that there is always a ready market for securities, they help prevent extreme price fluctuations and market gaps that can occur in less liquid markets. This liquidity provision is particularly crucial during market downturns or when unexpected news shocks the market, as it helps to cushion the impact of large trades or rapid shifts in market sentiment, thereby maintaining overall market stability.
Facilitating Trade Execution
For individual investors and institutional traders alike, the ability to execute trades efficiently and at predictable prices is a key aspect of market participation. Market makers enhance trade execution by reducing the bid-ask spread that traders encounter, thereby lowering the cost of trading and improving market efficiency. This liquidity provision ensures that trades can be executed quickly and at prices that closely reflect the current market valuation, benefitting all market participants by providing a more favorable trading environment.
Supporting Market Accessibility
By contributing to a more liquid and stable market, market makers also support greater market accessibility. They enable a wider range of participants, from retail investors to large institutions, to engage in trading activities with confidence, knowing that they can enter and exit positions as needed. This democratization of market access encourages participation and investment, contributing to the overall health and growth of the financial markets.
In essence, the roles and benefits provided by market makers are indispensable to the functioning of modern financial markets. Their activities support not only the operational aspects of trading, such as liquidity and efficiency, but also play a critical role in ensuring market stability, facilitating trade execution, and enhancing market accessibility. The smooth operation of financial markets relies heavily on the continuous and dedicated involvement of market makers, highlighting their fundamental importance in the trading ecosystem.
Visual Insights: Market Maker Influence
Pie Chart: Contribution to Market Liquidity
This pie chart shows the distribution of contributions to market liquidity, with market makers accounting for 60% and other participants making up the remaining 40%.
This significant contribution by market makers underlines their vital role in facilitating trading activities by providing the necessary liquidity for a smooth market operation.
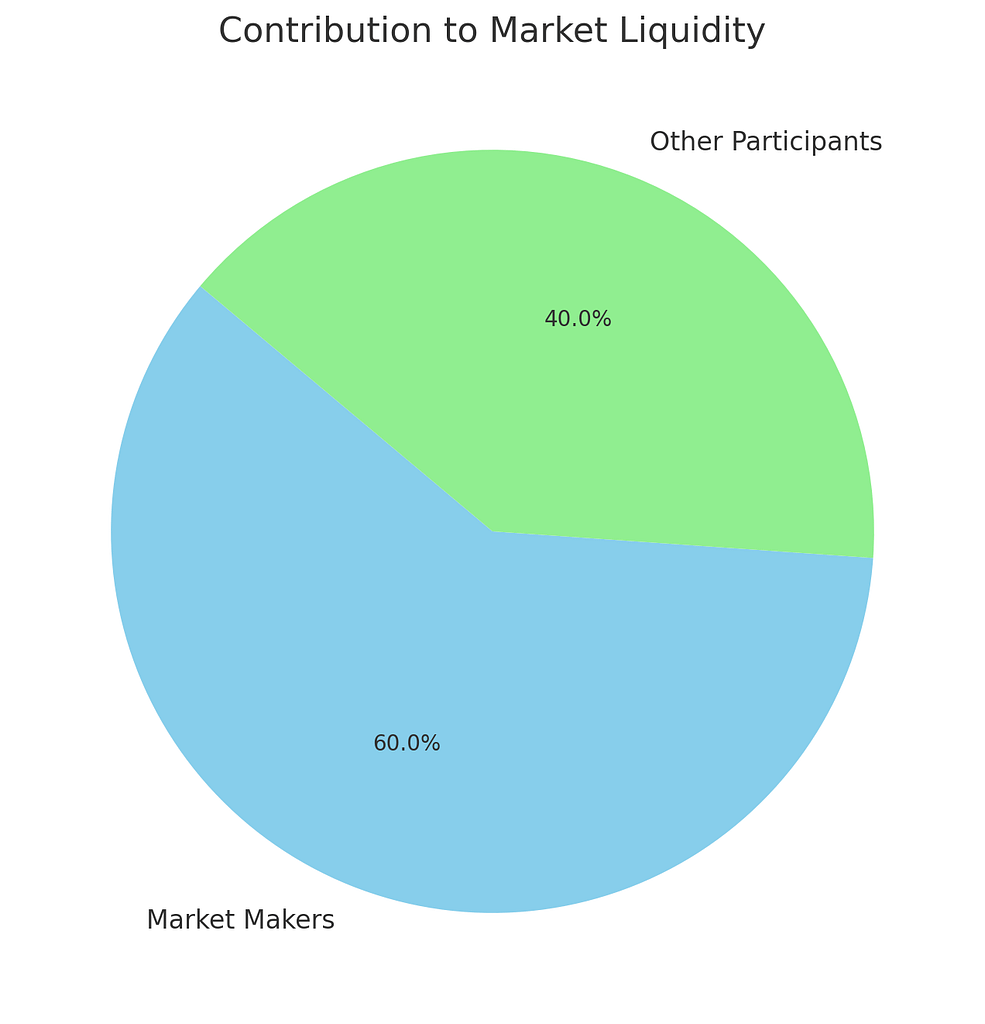
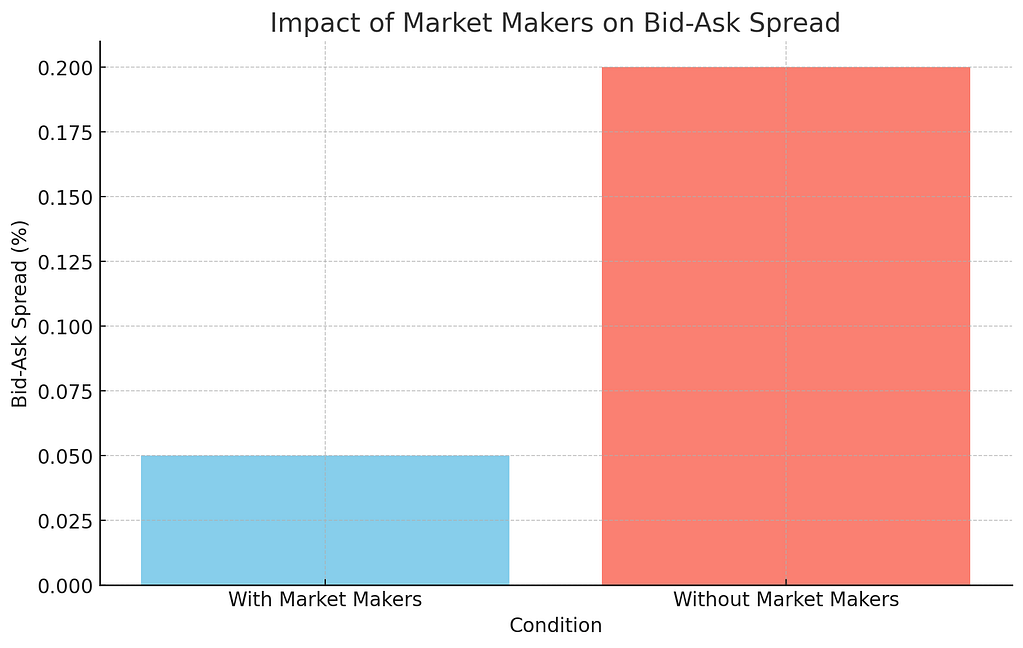
Bar Graph: Impact of Market Makers on Bid-Ask Spread
The bar graph demonstrates the effect of market makers on the bid-ask spread, comparing conditions with and without their presence.
With market makers, the bid-ask spread narrows to 0.05%, significantly lower than the 0.20% observed without them. This reduction in the bid-ask spread showcases the critical role of market makers in reducing transaction costs for traders, contributing to a more efficient and cost-effective trading environment
Personal Insights: The Indispensable Role of Market Makers
As an expert in the field, I’ve observed firsthand the indispensable role market makers play in the trading ecosystem. Their commitment to providing liquidity not only ensures that trades are executed efficiently but also contributes to the overall health and stability of the financial markets. In times of market stress, the presence of market makers can be especially crucial in preventing panic selling and excessive volatility.
Market makers also face their own set of challenges, such as managing large inventories of stocks and navigating rapid market movements. Their ability to balance these challenges while maintaining smooth market operations is a testament to their importance.
In essence, market makers are the unsung heroes of the financial markets. Their activities promote liquidity, reduce transaction costs, and ensure that markets remain orderly and functional. The trading ecosystem relies heavily on their contributions to maintain its vibrancy and efficiency.