
The stock market is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that plays a pivotal role in the global economy. It serves as a platform for companies to raise capital and for investors to buy and sell shares, thereby fueling economic growth and wealth creation. However, navigating the intricacies of the stock market can be daunting, especially for those new to the world of investing.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamental principles and mechanics of the stock market, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to make informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your journey, this article will provide valuable insights into the innerworkings of this fascinating financial arena.
| Participant | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Investors | Individuals or institutions that buy and sell stocks, seeking to generate returns on their investments. | Provide capital to companies to finance growth and operations. |
| Companies | Businesses that issue shares (stocks) to raise capital for growth, expansion, or other corporate purposes. | Raise capital to fund business activities and growth. |
| Brokers | Financial professionals or firms that facilitate the buying and selling of stocks on behalf of investors. | Execute buy and sell orders on behalf of investors and provide investment advice. |
| Market Makers | Institutions that provide liquidity to the market by quoting buy and sell prices for specific stocks. | Ensure market liquidity by providing bid and ask prices to facilitate trading. |
| Regulators | Government agencies or self-regulatory organizations responsible for overseeing the stock market and enforcing rules and regulations. | Ensure a fair, transparent, and well-regulated market to protect investors. |
This table provides an overview of the key participants in the stock market, briefly describing their role and function within the stock market ecosystem. Having an understanding of the different players involved is essential to fully comprehend the dynamics and workings of the stock market.
Understanding Stocks
At its core, a stock represents ownership in a publicly traded company. When you purchase shares of a company’s stock, you become a shareholder and partial owner of that business. As a shareholder, you have the potential to benefit from the company’s growth and success through capital appreciation (an increase in the stock’s value) and dividend payments (a portion of the company’s profits distributed to shareholders).
Stocks can be classified into different categories based on various factors, such as market capitalization (large-cap, mid-cap, or small-cap), industry sector (technology, healthcare, finance, etc.), or investment strategy (growth, value, or income).
Stock Exchanges
Stock exchanges are organized marketplaces where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. These exchanges facilitate the trading of securities and provide a regulated environment for buyers and sellers to interact. Some of the most prominent stock exchanges include:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
- NASDAQ
- London Stock Exchange (LSE)
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)
- Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
Stock exchanges operate under strict rules and regulations to ensure fair trading practices, transparency, and investor protection.
Key Stock Market Participants
The stock market is a dynamic ecosystem involving various participants, each playing a crucial role in its functioning:
- Investors: Individuals or institutions that buy and sell stocks, seeking to generate returns on their investments.
- Companies: Businesses that issue shares (stocks) to raise capital for growth, expansion, or other corporate purposes.
- Brokers: Financial professionals or firms that facilitate the buying and selling of stocks on behalf of investors.
- Market Makers: Institutions that provide liquidity to the market by quoting buy and sell prices for specific stocks.
- Regulators: Government agencies or self-regulatory organizations responsible for overseeing the stock market and enforcing rules and regulations.
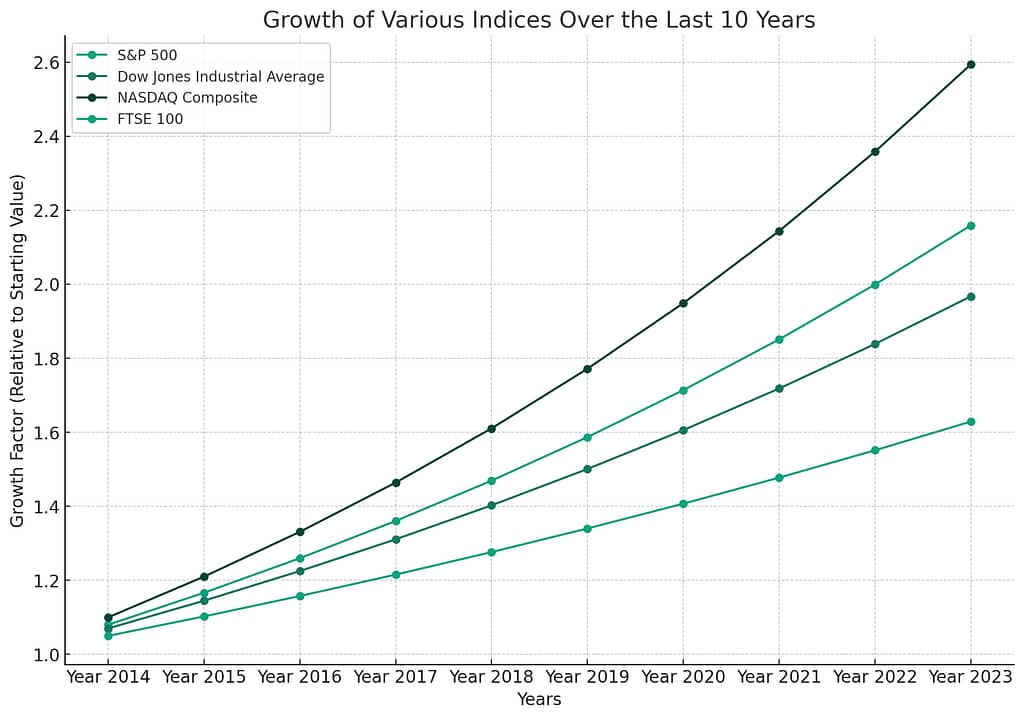
Stock Market Indices
Stock market indices are statistical measures that track the performance of a specific group of stocks. These indices serve as benchmarks for evaluating the overall health of the stock market and specific sectors or industries. Some widely followed indices include:
- S&P 500 (tracks the performance of 500 large-cap U.S. companies)
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (consists of 30 blue-chip U.S. companies)
- NASDAQ Composite (tracks the performance of companies listed on the NASDAQ exchange)
- FTSE 100 (represents the performance of the 100 largest companies listed on the London Stock Exchange)
Stock Valuation and Analysis
Investors often rely on various tools and methods to analyze and value stocks before making investment decisions. Two common approaches are:
- Fundamental Analysis: This involves analyzing a company’s financial statements, management, competitive landscape, and overall business performance to determine its intrinsic value.
- Technical Analysis: This approach focuses on studying historical price patterns, trading volume, and other market data to identify potential buy and sell signals.
Both fundamental and technical analysis can provide valuable insights into a stock’s potential performance, and many investors employ a combination of these methods to make informed investment decisions.
Risk and Diversification
Investing in the stock market inherently carries risks, such as market volatility, company-specific risks, and economic uncertainties. To mitigate these risks, investors often employ diversification strategies by spreading their investments across various stocks, industries, and asset classes.
Additionally, investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and time horizon when constructing their investment portfolios.
Conclusion
The stock market is a complex and ever-evolving landscape that offers numerous opportunities for wealth creation but also carries inherent risks. By understanding the fundamentals of stocks, exchanges, market participants, indices, valuation methods, and risk management strategies, you can navigate this intricate world with greater confidence and make informed investment decisions.
Remember, successful investing in the stock market requires continuous learning, discipline, and a long-term perspective. Seek guidance from financial professionals, stay up-to-date with market trends, and always align your investments with your personal financial goals and risk tolerance.